What is ESG?
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. It is a framework used to evaluate a company’s commitment to sustainable and ethical practices. This approach has gained significant importance as businesses and investors increasingly recognize the impact of ESG factors on long-term success and global well-being.
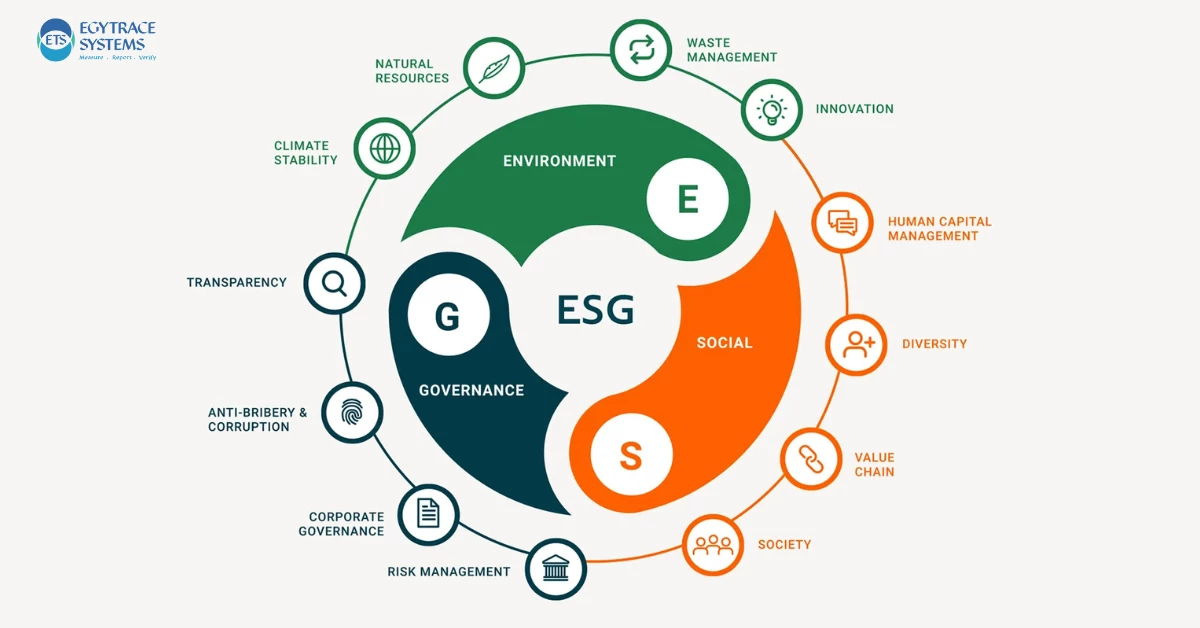
Understanding ESG: Breaking Down the Components
Environmental (E)
This component focuses on how a company addresses environmental challenges such as:
- Climate Change: Policies for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Resource Management: Efficient use of water, energy, and raw materials.
- Pollution Control: Initiatives to minimize waste and contamination.
Also :What is SECR Reporting?
Social (S)
The social aspect examines a company’s relationship with employees, customers, and communities. Key areas include:
- Employee Welfare: Fair wages, diversity, and safe working conditions.
- Community Engagement: Contributions to local development projects.
- Customer Relations: Ethical product sourcing and transparent communication.
Governance (G)
Governance evaluates the internal policies that ensure a company operates ethically and transparently. Key metrics include:
- Leadership Practices: Board diversity and executive accountability.
- Ethical Policies: Anti-corruption measures and compliance with laws.
- Transparency: Open and honest reporting of financial and operational data.
Why is ESG Important?
Businesses adopting ESG principles not only contribute to a sustainable future but also benefit in several ways:
- Enhanced Reputation: Companies with strong ESG practices attract positive public attention.
- Investor Attraction: ESG-aligned businesses appeal to socially conscious investors.
- Operational Efficiency: Sustainable practices often lead to cost savings and innovation.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating ESG risks reduces vulnerabilities.
ESG in Action: Examples of Impactful Practices
- Environmental: Implementing renewable energy projects.
- Social: Partnering with NGOs to support education initiatives.
- Governance: Establishing clear anti-corruption guidelines.
How ESG is Measured
ESG performance is evaluated using frameworks like:
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
- Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB)
- Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP)
These standards provide benchmarks for companies to align their goals and track progress.
The Role of EgyTrace in Promoting ESG
EgyTrace is a pioneering Egyptian company committed to helping businesses embrace sustainability. By offering advanced digital solutions and ensuring compliance with the EU Carbon Tax, EgyTrace empowers organizations to:
- Monitor emissions through automated MRV systems.
- Align operations with global ESG standards.
- Foster transparency and accountability in sustainability efforts.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing ESG principles is essential for companies aiming to thrive in today’s socially conscious world. Whether it’s reducing carbon emissions, ensuring fair labor practices, or maintaining transparent governance, adopting ESG practices positions businesses as leaders in sustainability.
Looking to integrate ESG into your business operations? Contact EgyTrace today to discover how our solutions can help you achieve your sustainability goals while complying with global standards.